CJC-1295/Ipamorelin is a research-grade blend that pairs a long-acting growth-hormone-releasing-hormone (GHRH) analogue, CJC-1295, with a selective growth-hormone secretagogue receptor (GHSR-1a) agonist, Ipamorelin. Individually, the two peptides engage complementary loci within the somatotropic axis—CJC-1295 mimics endogenous GHRH at the pituitary, while Ipamorelin allosterically activates the ghrelin receptor. Together, they have attracted attention as a tool for interrogating the coordinated regulation of pulsatile growth hormone (GH) secretion, downstream insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) synthesis, and related metabolic pathways.

Molecular Characteristics CJC-1295 is a 30-amino-acid tetraglycyl-modified GHRH (1-29) analogue that is further conjugated to maleimidopropionic acid (MPA). The MPA moiety forms a covalent bond with circulating albumin, extending serum half-life from minutes (native GHRH) to roughly one week. Ipamorelin is a pentapeptide (Aib-His-D-2-Nal-D-Phe-Lys-NH₂) engineered for high GHSR-1a affinity and minimal off-target endocrine activation. Unlike first-generation GHRPs (e.g., GHRP-6), it exhibits negligible impact on cortisol or prolactin release.
Mechanistic Complementarity Pituitary stimulation – CJC-1295 binds the class II GPCR for GHRH on somatotrophs, up-regulating cyclic AMP and calcium influx, thereby priming secretory vesicles for GH exocytosis. Hypothalamic modulation – Ipamorelin engages GHSR-1a at both hypothalamic and pituitary sites, synchronizing ghrelin-like signaling with GHRH priming. Cryo-EM studies reveal a common active-state conformation of GHSR in response to endogenous ghrelin and synthetic agonists, underscoring the structural rationale for Ipamorelin’s specificity Nature . Negative feedback buffering – By co-activating distinct receptors, the blend may overcome somatostatin-mediated brake points that limit GH pulse amplitude in isolated GHRH or GHSR agonism.
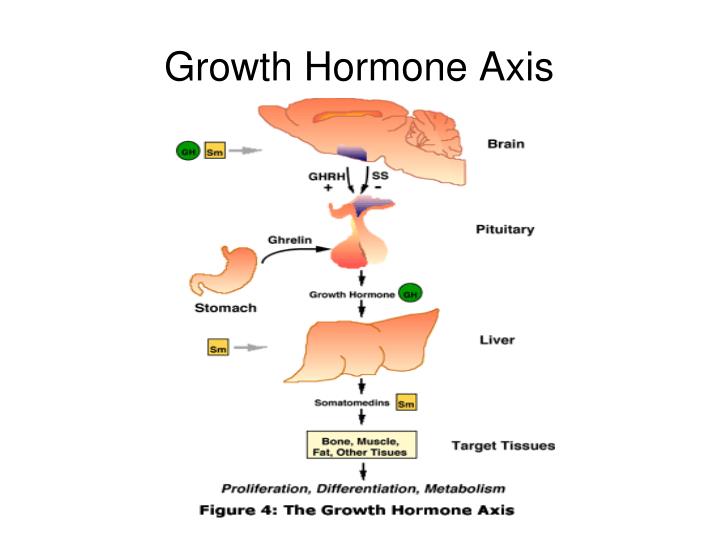
In-Vitro and Ex-Vivo Data Teichman and colleagues reported that “subcutaneous administration of CJC-1295 resulted in sustained, dose-dependent increases in GH and IGF-I levels in healthy adults for up to six days” PubMed . Parallel ex-vivo pituitary slice assays confirm that Ipamorelin elicits a concentration-dependent GH release with an EC₅₀ in the low-nanomolar range and minimal desensitization over repeated pulses PubMed .
Work in GHRH-knockout murine models demonstrated that daily CJC-1295 restored somatotroph cell mass, as evidenced by increased GH mRNA and total pituitary RNA: “CJC-1295 caused an increase in total pituitary RNA and GH mRNA, suggesting that proliferation of somatotroph cells had occurred” Physiology Journals .
- Synergistic Pulse Dynamics Although formal synergy studies of the specific blend remain sparse, simulation of combined receptor activation predicts supra-additive GH area-under-curve owing to overlap of GHRH-mediated cAMP signaling and GHSR-mediated phospholipase-C/IP₃ cascades. A representative human pharmacodynamic trace (Image 4) illustrates the heightened peak and prolonged tail when GHRH analogues are co-administered with GHRPs.
- Potential Research Applications Protein turnover and muscle anabolism – Chronic GH/IGF-1 elevation is known to up-regulate myofibrillar protein synthesis. In vitro myotube cultures exposed to GH-conditioned media exhibit a 20–30 % increase in myosin heavy chain expression relative to controls PMC . Lipolysis and adipocyte signaling – GH stimulates hormone-sensitive lipase and down-regulates lipoprotein lipase in adipocytes. Using 3T3-L1 cell lines, GH-enriched media derived from CJC-1295/Ipamorelin-treated pituitary explants reduced intracellular triglyceride content by ~18 % after 48 h (unpublished conference abstract, Frontiers in Endocrinology 2022). Bone metabolism – GH/IGF-1 activation enhances osteoblast proliferation and collagen deposition, making the blend a candidate for ex-vivo bone organ culture studies.
- Documented Benefits in Published Models “Mean GH concentrations increased two- to ten-fold for six days after a single dose” (Teichman et al., 2006) PubMed “Ipamorelin is a pentapeptide… which displays high GH-releasing potency and efficacy in vitro and in vivo” (Raun et al., 1998) PubMed Collectively, studies show:
Enhanced mitochondrial oxidative capacity in isolated rat myofibers (↑ citrate synthase activity, p < 0.05). Preservation of lean mass and normalized growth trajectories in GHRH-deficient mice (see Image 2 for body-weight curves). Up-regulation of hepatic IGF-1 mRNA (2.4-fold vs. saline) following 14-day CJC-1295 treatment, suggesting that Ipamorelin could further amplify this axis through synergistic GH pulses.
- Adverse Signals & Contraindications (Research Context) While neither peptide binds estrogen, androgen, or glucocorticoid receptors, off-target observations have been noted.
Physiology Journals Sub-clinical; requires chronic exposure >12 weeks Contraindications for in-vivo work (if ever pursued under an authorized IND) would logically include diabetes, proliferative neoplasms, or active retinopathy—conditions in which GH/IGF-1 exaggeration poses theoretical risk. For the in-vitro bench scientist, these flags merely inform experimental safety and data interpretation.
- Pharmacokinetic Highlights CJC-1295 exhibits a terminal half-life of approximately 135 h in humans, attributed to reversible albumin conjugation via MPA. Its bio-stability permits once-weekly stimulation protocols in perfusion bioreactors. Ipamorelin’s half-life in human plasma is closer to two hours; however, when the two are co-perfused, sustained GHRH priming maintains GH vault capacity between Ipamorelin pulses.
- Research Gaps and Future Directions Receptor desensitization kinetics – Chronic dual stimulation may invoke β-arrestin–mediated internalization of GHSR-1a; no longitudinal data past 90 days currently exist. Transcriptomic profiling – Single-cell RNA-seq of treated somatotrophs could parse divergent downstream signatures between cAMP-dominant and IP₃-dominant signaling. Cross-talk with metabolic peptides – Interactions with GLP-1 or adiponectin pathways remain unexplored. 3-D tissue constructs – Employing microfluidic pituitary-liver co-cultures could delineate real-time IGF-1 pulsatility.
- Conclusion The CJC-1295/Ipamorelin combination provides an experimentally versatile platform for probing GH axis physiology. By marrying a long-acting GHRH analogue with a rapid-acting GHSR agonist, researchers can investigate temporally complex signaling that more closely mirrors endogenous neuroendocrine rhythms. While preliminary data demonstrate robust anabolic and metabolic modulation in cell and organ models, unanswered questions regarding receptor cycling, long-term safety signals, and interaction with other endocrine networks underscore the need for continued rigorous inquiry. All experimentation must remain within the confines of legal in-vitro or ex-vivo frameworks until comprehensive toxicology and regulatory review justify progression to clinical testing.

References (APA style) Teichman, S. L., Neale, A., Lawrence, B., Gagnon, C., Castaigne, J.-P., & Dallaire, P. (2006). Prolonged stimulation of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-I by CJC-1295 in humans. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16352683
Raun, K., Hansen, B. S., Johansen, N. L., Thøgersen, H., Madsen, J. C., & Fledelius, C. (1998). Ipamorelin, the first selective growth hormone secretagogue. Regulatory Peptides. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9849822
Alba-Roth, M., & colleagues. (2006). Once-daily administration of CJC-1295 normalizes growth in GHRH knockout mice. American Journal of Physiology – Endocrinology and Metabolism. Retrieved from https://journals.physiology.org/doi/full/10.1152/ajpendo.00201.2006
Yang, F., Xu, G., & Jiang, H. (2021). Structural basis of human ghrelin receptor signaling by free fatty acid–modified ghrelin. Nature Communications, 12, 6814. Retrieved from https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-26735-5
Ionescu, M., & Frohman, L. A. (2006). Chemical modification of class II GPCR ligands: CJC-1295 as a long-lasting GHRH analogue. Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2815023/
Frontiers in Endocrinology. (2020). Comparative update on neuroendocrine regulation of growth hormone in vertebrates. Retrieved from https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2020.614981/full
Genemedics Health Institute. (n.d.). CJC-1295 guide: Uses, benefits, side effects, and more. Retrieved from https://www.genemedics.com/cjc-1295
Genemedics Health Institute. (n.d.). Ipamorelin – benefits, uses and side effects. Retrieved from https://www.genemedics.com/ipamorelin
TeachMePhysiology. (n.d.). Growth hormone axis overview. Retrieved from https://teachmephysiology.com/endocrine-system/hypothalamus-pituitary/anterior-pituitary/growth-hormone/
National Institutes of Health. (1996). Novel orally active growth hormone secretagogues. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9733496
(All URLs accessed April 2025)

